

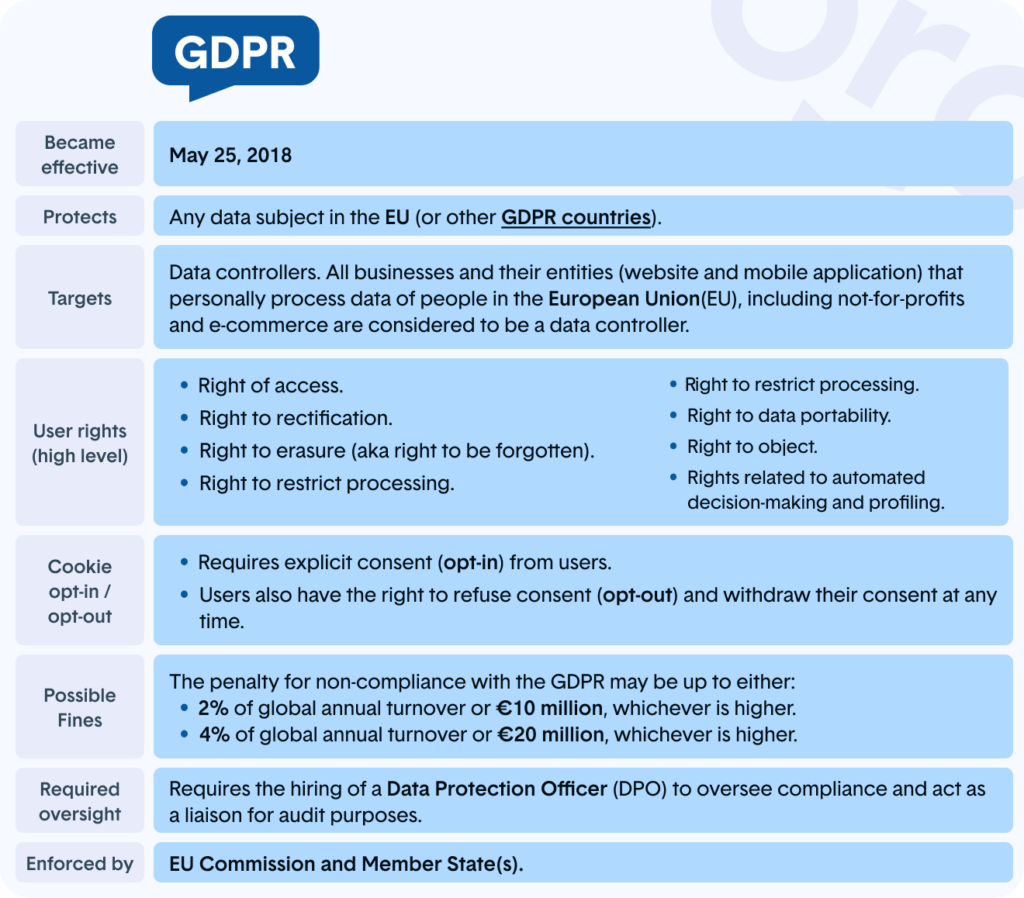
GDPR, or the General Data Protection Regulation, sets the bar for privacy and data protection worldwide. Complying with GDPR means ensuring that personal data is processed lawfully, transparently, and securely.
GDPR came into effect in 2018, significantly changing how organizations manage personal data. GDPR empowers individuals (particularly EU citizens) to control their data. GDPR compliance is vital for organizations that process personal data, as it safeguards the data, ensures transparency in data handling, and adheres to recognized global data protection norms.
Understanding the key components of GDPR is central to achieving compliance. These key components include:
Under GDPR, it’s important to limit data collection to what is necessary for the purposes for which it is processed. Organizations that gather personal data must ensure its accuracy and timely updates to maintain data integrity and dependability.
Moreover, GDPR bestows individuals with the right to control their personal data, including access to data, data rectification, and the right to erasure. The roles of a Data Controller and a Data Processor are also crucial components of GDPR. The Data Controller is responsible for determining the methods and purposes of processing personal data, while the Data Processor is tasked with the maintenance and processing of personal data records.
GDPR outlines seven principles that govern data protection:
These requirements apply to all types of personal data and play a crucial role in ensuring data privacy and GDPR compliance. They are designed to safeguard personal data, protect the rights of individuals, and ensure that their personal data is handled responsibly.
The concept of data protection by design and by default is integral to these principles. It involves integrating data protection into processing activities and business practices right from the design stage and throughout the entire data processing lifecycle. The objective is to ensure that organizations selectively gather, handle, and retain solely the essential personal data required to deliver an agreed-upon service and impose safeguards when necessary, such as obtaining consent prior to disclosing personal data to a third party.
In addition, organizations are required to implement suitable technical and organizational measures to guarantee a level of security commensurate with the associated risks. These measures should safeguard personal data from:
Under GDPR, data subjects are endowed with eight specific rights:
These rights empower individuals, giving them control over their personal data.
A formal request made by an individual to a company seeking information that the company holds about them is known as a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR). Organizations are obligated to respond to these requests within one month as per GDPR. Managing DSAR requests entails overseeing the complete request workflow, from initial intake to fulfillment, and ensuring adherence to GDPR’s privacy rights regulations.
Under GDPR, organizations must fulfill strict personal data processing requirements. To process personal data, it is necessary to obtain explicit consent from the data subject, which should be:
This consent indicates the data subject’s agreement to the processing of their personal data.
Additionally, organizations are required to document processing activities in their records of processing activities and conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) to evaluate the risk to individuals.
GDPR applies to the processing of EU residents’ personal data by any organization (including U.S. and Canadian organizations), regardless of where data processing occurs.